


Abstracts,
Organizers,
Progr. Comm.,
Org. Comm.,
From The...,
Statistics,
| A-B, |
C, |
D, |
F-G, |
J, |
K, |
L, |
M, |
N, |
O, |
P, |
R, |
S, |
T, |
W, |
Z, |

DYNAMIC PROCESSES SIMULATION

| Polish Electrical Engineering Society - Warsaw Section in association with the |
| Electrical Engineering Department of Warsaw Technical University |
| Roman BARLIK
Jan KACPRZAK Tadeusz KACZOREK Jerzy KLAMKA Andrzej KŁOS Stanisław KRZEMIŃSKI | Prof.
Prof. Prof. Prof. Prof. Prof. | Adam MAJEWSKI Jerzy MARYNIAK Ryszard TADEUSIEWICZ Piotr TATJEWSKI Zdzisław TRZASKA Jerzy WRÓBEL | Prof. Prof. Prof. Prof. Prof. Prof. |
| Andrzej | MARUSAK | Ph.D. | (Chairman) |
| Ryszard | NIEDBAŁA | Ph.D. | (Secretary) |
| Włodzimierz | KAŁAT | Ph.D. | |
| Piotr | MARUSAK | M.Sc. | |
| Wiesław | MYRCHA | Ph.D. |
All enquires concerning the Conference should be addressed to SECRETARIAT:
Polish Electrical Engineering Society - Warsaw Section,
Gm. Glowny, pok.245,
Pl. Politechniki 1, PL-00-661 Warszawa, Poland.

Dear Sir or Madam
The conferences on 'Dynamic Processes Simulation' -
SPD
have been organized since 1980.
The first symposium in cycle SPD was organized
on June 1980 in Kalatówki, the High Tatra
Mountains. The next 8 symposiums were organized on June 1985,
1986, 1987, 1988, 1990, 1992, 1994 - in Polana Chochołowska, and 1996 in Kościelisko, the West Tatra Mountains.
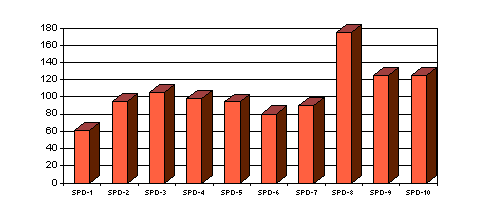
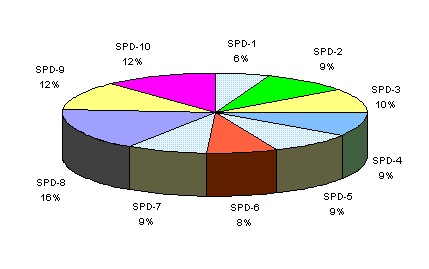
Many persons took part in these conferences, suitably: 62, 95, 105, 98, 94, 81, 90, 176 and 125. They were generally from Poland and few from the DDR, USA, Czechoslovakia, USSR, Egypt, Jordan, Syria, Nigeria, Russia, Madagascar, and Bangladesh.
125 persons from Poland will take place in the most recent conferences. The conferences are planed in XVI scientific sections. 15 minutes will be assigned for the presentation of one paper. A 5 minute discussion will follow the presentation. The Organizing Committee reviewed 64 scientific papers. 63 are qualified for presentation.
This set of abstracts contains the summaries the papers qualified for presentation at SPD-10 in alphabetical order. Name index of the authors and participants is enclosed at the end of set. The opening of the SPD-10 is planned to take place on June 15, 1998 at 9:30 a.m.
An excursion into the beautiful Slovakia Tatra Mountains will be arranged. We have planned a camp fire with beer, sausage and pig roast on Monday, June 15, 1998 at 19:30 p.m.
I wish you all successful paper presentations, fruitful discussion,
and beautiful weather!
Warsaw, May 29, 1998

ABSTRACTS of PAPERS
(ISBN 83-909385-0-2)
SPD CONFERENCE ANNIVERSARY SESSION
*. Andrzej Marusak, Piotr Marusak (Warsaw Technical University)
HISTORY OF "DYNAMIC PROCESSES SIMULATION" MEETINGS - FROM SPD-1 to SPD-10
The SPD symposiums have been organized since 1980.
The paper presents some interesting historical and statistical
information about them. Enclosed are science committee compositions,
complete lists of participants and printed papers from SPD-1 to
SPD-10. Some interesting analytic information about SPD conference
has also been included.
SIMULATION INVESTIGATIONS ON A STATISTICS SERVER ARCHITECTURE
The paper presents an idea of a statistics server which is used for creating multidimensional histograms for large relational databases. The three tier architecture (in opposite to client-server software architecture) of the statistics server was considered for improving the performance of a system. The main multithreaded program of statistics server is the second tier which runs with a database server program (the third tier) on the same computer and which communicates with statistics client applications (the first "thin" tier) using TCP/IP protocol.
The article presents an idea of a fast statistics
server which makes histograms approximately using only a samples
from database and gives confidence intervals to user. The method
of random sampling from database through B+ index trees was shown.
The simple method of constructing confidence intervals using properties
of binomial and normal distribution was described.
2. Janusz Baran, Robert Bąbka, Mariusz Matyjasik,
Technical University of Częstochowa
SIMULATION OF PROCESSES FOR COMPUTER-AIDED DESIGN OF CONTROL SYSTEMS WITH PLC CONTROLLERS
The paper deals with an idea of visualization and
simulation of process for computer-aided design of control systems
with PLC controllers. Computer models of controlled processes
with animation and sound effects were created using LabVIEW graphical
programming environment. They run on a PC computer equipped with
a data acquisition & control card which is electrically coupled
with an external controller. The models include some diagnostic
features, eg. they can signalize control errors, which is useful
at the stage of control algorithm development and for teaching
of PLC programming. Two examples of applications are presented
in the paper: a filling and mixing station for pure logic control
and a two tanks system dynamic model for analog and logic control.
Some problems connected with on-line simulation of a model dynamics
are considered.
3. Tadeusz Banek (Tech.
Univ. of Lublin), Tomasz Goetzendorf-Grabowski
(Warsaw Univ. of Technology),
Jacek Goszczyński (Institute
of Aviation), Jerzy Maryniak (Institute
of Aviation, Warsaw
Univ. of Technology), Józef
Pietrucha (Warsaw Univ. of Technology),
Jarosław Pyrz (Institute of Aviation)
OPTIMAL FILTER THEORY IN DEVELOPED TO THE ALGORITHM OF THE PARAMETER IDENTIFICATION OF FLYING OBJECT
In this paper was presented an assumption and method of optimal filter theory in developed to the algorithm of the parameter identification of flying object. The algorithm which we work out will be use to the numerical simulation of flight in future.
Mathematical model of the aircraft (6DOF) was transform to optimal filter theory requirement form (defined by Lipcer R. S. and Szirajew A. N. in theirs monograph). In the paper was presented a reasons and method to receive of a basic dependencies leading to solution of the problem. Practical application of presented algorithm was tested by the simple test example show in the paper.
This work was supported by Polish State Committee
of Scientific Research in 1995 - 1998 (grant no. 9T12C 006
08).
4. Tadeusz Bartkowski,
Gdańsk University of Technology
NUMERICAL SOLUTIONS OF ORDINARY DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS USING MODIFIED KROGH ALGORITHM
The main aim of the paper is the presentation of
the new numerical integration procedure BGKODE. This procedure
has elaborated by authors of this paper and Marek Korniak. The
main codes of this procedure are: the integrator BGKSTEP, the
interpolation routine BGKINTRP, the driver BGKDE and the memory
allocation routine BGKMA. The paper describes the structure of
the integrator and presents the comparison of three procedures:
BGKODE, DIFSUBB (Gear) and ODE (Shampin-Gordon). For the testing
the accuracy and numerical efficiency of them two (exponential
and harmonic oscillator) ordinary differential equations are used.
The results of numerical tests are quite positive for all procedures
but in the testing areas BGKODE is more efficient than others.
6. Janusz Bidziński,
Warsaw University of Technology, Institute of Vehicles
MODELING AND SIMULATION OF TRANSITION PROCESSES IN TRACTOR DRIVING SYSTEM
Model and results of computer simulation of four-wheel
drive agriculture tractor driving system are presented in the
paper. The tractor is equipped with a transmission gearbox allowing
to shift gear under load and controlled by a set of friction clutches.
The mathematical description of friction clutches operations,
tractor wheels cooperation with ground and the tractor load caused
by working tool adopted in the model takes into account different
operational states corresponding to movement, stopping and changing
direction of the relative motion of elements in contact. This
results in a set of equations of motion with discontinuous right-hand
sides. Some results of simulation of transition processes during
moving, stopping and changing gears without the break off in power
transmission are presented.
7. Zygmunt Biernacki,
Marek Kurkowski, Piotr Rakus, Technical University of Częstochowa
STATIC THREE-PHASE UPS SYSTEM AS A DISTORTION POWER COMPENSATOR OF A NON-LINEAR THREE-PHASE RECEIVER
The article discusses possibilities of employment of a static three-phase UPS system for compensation of distortion power in electric power mains. Distortion power is connected with power supply of a non-linear three-phase receiver which is composed of RL type load with diode for each phase. Non-linear three-phase symmetric and non-symmetric load will be taken into account. Operation of static UPS system facilitates not only distortion power compensation but also provision of symmetric three-phase load of electric power supply mains.
Assessment of respective circuits will be effected
on the basis of TCAD 6.2 simulation software package, which facilitates
complete simulation for a three-phase UPS system as well as Fourier's
analysis for resulting current and voltage characteristics (power
supply from mains with and without compensation).
9. Janusz Buchta, Janusz Skierski,
Łódz University of Technology
DYNAMIC PROCESSES IN AUXILIARY ELECTRICAL SYSTEM OF POWER UNIT DURING POWER DROP
The operation of the power unit following power drop
to the load of auxiliaries is an interesting state both in practical
and scientific meaning. The generator operates asynchronously
in weak and single power system. The task to keep up the power
unit in operation in this state requires to prepare many facilities
including auxiliary electrical system. Simulation of dynamic processes
in such a system is a valuable supplement of an expensive experimental
investigations. Mathematical model of the system includes models
of its components: steam turbine, generator, speed governor, excitation
controller, induction motor and auxiliaries. Authors worked out
mathematical model and computer program for analyzing operation
of auxiliary electrical system during power drop. The paper presents
results of simulation for the 360 MW power unit.
10. Artur Chorążyczewski,
Wrocław University of Technology
VISUALIZATION OF THE PHENOTYPIC EVOLUTION WITH THE MODULE OF STATISTICAL ANALYSIS
Visualization of evolutionary algorithms might be
of great help to the researchers and students in the area. Dynamics
of evolving populations is somewhat complicated and visualization
helps to establish proper intuitions. Yet, one has to be careful
when generalizing such observations, as evolution strongly depends
on chance and particular simulation runs might differ very significantly
from each other. Therefore, a good visualization program should
have a statistical module that would allow for testing of assumed
generalizations. Such a program - developed for simulation of
phenotypic evolution in multidimensional real spaces - is presented,
together with some examples of its applications.
11. Henryk Chrostowski,
Zygmunt Popczyk, Wrocław University of Technology
SOME FEATURES OF A CANONICAL FORM METHOD FOR SOLVING - PROGRAMMING ODE
In many mathematical models a forcing function, then consequently the right side of an ordinary differential equation (ODE), is formed with the function and its derivatives.
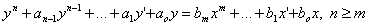
In the analog computer there are exact integrating elements, however, differential elements can fulfill operations with big approximation. Then, the most efficient way of programming - constructing the analog scheme - is the canonical form method.
This method, contradicting the general method, does not give the opportunity for the observation of the derivatives of the solution, but only of the function y. Many of the models describing the work of a hydraulic system stress that the necessary issue is the knowledge of the current derivative value.
The work presents a feature of the canonical form
method enabling the direct observation of the function y and its
derivatives for some specified conditions up to the grade of n-m
(inclusive). The solution was illustrated with the example of
modeling valves of a piston pump with the help of analog-hybrid
computer WAT 1010A.
12. Henryk Chrostowski, Krzysztof Kędzia,
Wrocław University of Technology
MODELING OF ENERGY SAVING MULTISOURCE HYDROSTATIC POWER TRANSMISSION SYSTEMS
The paper presents the analysis and simulation of the hydrostatic transformation system and energy distribution transmission. For multisource hydrostatic systems in with the load is given in the form of cycle, a method of determining optimal parameters of stabilized working of the initial source engine and the hydraulic accumulator is presented as well.
Simulation was make in simulation program SIMULINK.
In the paper was presented structure of simulation model and carefully
selected simulations graphs too.
13. Zdzisław Dąbrowski, Jacek Jusis,
Witold Marowski, Warsaw University of
Technology
SIMULATION OF THE INTERACTION BETWEEN A PRODUCTION LINE AND A TRANSIT STORE WITHIN A RELATIONAL DATABASE APPLICATION
Transit stores are elements of many production lines, e.g. silos placed within a production line in chemical works. Therefore, if a relational database application for production planning in such plant is developed, the logical structure of its database must make possible to simulate the simultaneous acting of a production line and any of its transit stores. The production line interacts with a transit store by means of filling and making empty processes. Some considerations concerning this problem are given in the paper.
The production line interacts with a transit store by means of filling and making empty processes. It has been assumed that any of these both processes can consist of any number of sections with the constant product volume rates. Any number of these processes can be active in the same time towards a given transit store. The purpose of the set of subroutines, which is described in the paper, is to test, whether it is possible to place two coupled filling and a making empty processes associated with a given order within existing time gaps, while another interacting processes have been defined already. The basic assumptions and methods of the testing process, the use of the SQL language queries as well as the structure of the database table used to store data of all processes are described in the paper.
The code of the database application described in
the paper has been written in the object-oriented programming
language Visual Basic for Applications and the application has
been developed in the Microsoft Access program.
14. Bogusław Dołęga, Tomasz Rogalski,
Rzeszów University of Technology
THE MICROCOMPUTER LABORATORY STAND FOR DEVELOPING AND TESTING AIRCRAFT CONTROL AND NAVIGATION SYSTEMS
This paper includes a conception and practical realization
of the simulation laboratory stand for developing and testing
aircraft control and navigation systems. The basic assumptions
of using models of airplane, weather noising, flight control and
measurement systems are appeared. This stand was used to prototyping
APC-4 "SkyGuide" - control and navigation system for
unmanned flying vehicles. The work reported here has been done
within the framework of KBN Research Project under grand number
DB/9 T12C 011 08/TA.
15. Domagała Z., Prokopowicz J., Sradomski
W., Wrocław University of Technology
SIMULATION STUDY OF THE PROPORTIONAL RELIEF VALVE
The mathematical model of the proportional relief
valve, model UZPPE 6 is presented in the paper. It is solved owing
to the simulating system "SIMULINK" using the IBM PC
computer. The valve constructional parameters, which have an influence
on the dynamic characteristic as a result of the examinations,
are defined. In the model the pump delivery has been token into
account. The conclusions and the future trends study are worked
out.
16. Ignacy Dulba, Wrocaw
University of Technology
KINEMATIC CALIBRATION OF A ROBOT MANIPULATOR
A task of kinematics calibration is to determine
real kinematics parameters of a manipulator (lengths of links,
angular displacements) based on experiments carried out on the
object. Accuracy of calibration is vital in trajectory (path)
planning or tracking. In this paper two calibration methods have
been presented. First method is a least square method applied
at a workspace of the manipulator. Second one is based on a Newton
algorithm of solving an inverse kinematics task. In the Newton
method, local estimates of kinematics parameters are weighted
using coefficients derived from a Jacobean matrix of the manipulator.
These methods have been illustrated on a double-pendulum manipulator
and their features have been discussed.
17. Marek Durnaś, Adam Żuchowski,
Szczecin University of Technology
THE SIMULATION OF "STEP BY STEP" CONTROL OF SHIP MOVEMENT ALONG THE ASSUMED TRAJECTORY
The problem of control ship movement along assumed trajectory becomes extremely difficult in case of complicated shape of trajectory. The complicated shape of required trajectory is generated by such external circumstances like possibility of collision necessity of passing by the dangerous objects, etc., The mentioned circumstances reveal all maneuver errors. On the other hand the saving of energy (fuel) under above conditions is usually neglected.
The paper contains the proposal of method for calculation of such control inputs that energy needed for displacement of ship along of trajectories of complicated forms is minimized. The control inputs are determined for sections of assumed trajectory then results of calculation are consecutively "stitching".
Results obtained in previous step are used for correction
of following step. Thus, the control process is similar to "impulse"
one. The simulation carried out under "heavy" assumption
confirm that method can be successfully applied to control of
ship movement
18. Przemysław Dziemieszkiewicz, Roman Galar,
Wrocław University of Technology
SIMULATION OF DIVERSIFICATION OF POPULATIONS EVOLVING IN A MOSAIC ENVIRONMENT
An important aspect of evolution is that fitness depends as much on traits of an individual as on characteristics of the niche occupied by this individual.
We assumed a simple selection-mutation model of an asexual population evolving in a mosaic environment with two kinds of niches. Our aim was to define conditions, under which the distribution of evolving population becomes bimodal, thus reflecting the different adaptive preferences of both niches. In a number of simulation experiments we have found that such diversification is only possible with competitive selection of the fight for survival type. With the protection type selection, which is based on parental fitness, population might become well adopted solely to one of the niches.
In the context of evolutionary market models this
seems to agree with observations that the advertisement based
economy is promoting uniformity rather than diversity of goods
and services.
19. Jan Francyk, Zbigniew Rodziewicz,
Wrocław University of Technology
EMULATION OF TELECOMMUNICATION TERMINAL ON PC
A terminal is one of the main elements of telecommunication network. Nowadays telecommunication terminals are not only phones but also complexity devices which thanks technological progress enables access for many services offered by telecommunication operators.
Now, the increasing of possibilities of telecommunication terminal based not only on hardware but in many situation on extension of existing software.
In the paper authors present idea of emulation of
multifunction telecommunication terminal, which except commutation
and telecommunication functions is design also for additional
services. The advantages of object oriented programming and C++
language useful for emulation are presented, too.
20. Wiesław Galor, Jerzy Hajduk,
Szczecin Maritime University
SIMULATION OF MOVEMENT OF HYDRAULIC JET PROPULSION VESSELS IN THE CONTEX OF DETERMINING SAFE MANOEUVRING CONDITIONS
Putting into use the sailing craft of water jet propulsion causes a number of new problems. The problems result from the necessity of ensuring a proper level of safety. It refers to both sailing craft and the areas in which it is operated. The problems differ depending on a type of water area. In the restricted areas, including port areas, the dominating problems are connected with the safety of the craft. The analysis and determination of safe maneuvering conditions with deterministic methods is not very effective. The reason is a big number of new variables occurring in the process. The use of simulation methods enables a complex collection of experimental material and multi -criterion analysis of the results.
The simulation of movement of a water jet propulsion has been used in connection with the operation of the catamaran "BOOMERANG" put into use winoujście - Malmoe route. The catamaran, propelled with four water jet engines, reaches a speed of over 40 knots. A new concept of steering the propulsion - helm devices changes the former principles of maneuvering. The speeds of ejected water jets, with improper use of steering sets, may distinctively affect the existing hydrotechnical structures. There are questions the answers to which will make it possible to decide whether to accept the craft of this type in traffic or not. The decision takes into account and specifies safe maneuvering conditions.
The paper presents a principle of water jet propulsion,
a concept of steering the craft with such propulsion, a method
of simulation tests and the results obtained for the catamaran
"BOOMERANG" maneuvering in the port of winoujście.
21. Konstanty Gawrylczyk,
Szczecin University of Technology
ANALYSIS OF ELECTROMAGNETIC FIELDS WITH SPICE
This paper presents a method of electromagnetic fields analysis using SPICE-package. The described method matches static and stationary field problems. However, it can be extended on time domain problems. Main advance of this method is the possibility of the sensitivity analysis.
When designing an electrical apparatus, it is usually necessary to know, how the magnetic field distribution, or its integral value will change depending on small changes of material parameters , , . This is the task of sensitivity analysis. Well known method bases on Tellegen-theorem. Main applications of this method for field tasks are shape and conductivity recognition, and shape optimization. All of them are carried out in iterative manner, taking either sensitivity value or error gradient as search direction for global minimum. The described method is very effective numerically, when using band matrices and Cholesky-decomposition. However, common finite element packages have no possibility of sensitivity analysis.
For the application of the network theory we should
first find the network model, which is equivalent to the finite
element model. The input data of this model are then transferred
to the SPICE. This calculates
nodal potentials, as well as sensitivity values for chosen element
parameters. In numerical examples the results obtained with the
help of network model of finite elements are shown.
22. Zbigniew Goryca, Technical
University of Radom
SIMULATION TESTS OF STARTING OF TWO BANDS BRUSHLESS MOTOR WITH PERMANENT MAGNET
The results of simulation for starting the Brussels
motor with permanent magnet placed on the rotor have been presented.
There has been also presented mathematical model of such kind
of motor. There has been worked out simulation model on the basis
of the mathematical model and simulation of motor starting has
been also realized. There has been determined the dependence of
instantaneous moment generated by the motor on switching angle
at which the voltage system supplying the bands of motor winding
is changed. The value of that angle has, an influence on the moment
generated by the motor and also it has an influence on motor speed.
Those dependencies are shown in diagrams. There has been concluded
that the current position of rotor relative to the stator must
be determined more precisely.
23. Jerzy Graffstein, Mariusz Krawczyk, Jerzy
Maryniak, Institute of Aviation, Warsaw
INFLUENCE OF DISTURBANCE ON EFFECT OF SYMULATIONS SPECIAL MANOEUVRE UAV
The paper deals with the simulation problem of aircraft general motion. Equation of motion have been derived by application of the Boltzmann-Hamel equations. Model will be useful to develop flight control systems based upon the non-linear inverse dynamic, which may provide improved level of safety and performance over the conventional designs.
Some results of numerical simulations special maneuver
(take-off) UAV in longitudinal channel are reported.
24. Jerzy Gustowski, Andrzej Marusak,
Warsaw University of Technology
LINEAR DC MOTOR MODELING AND STATIC DRIVING FORCE IDENTIFICATION
The paper describes the idea of modeling and identification of a linear DC motor. That motor has been used to drive a mechanical laboratory object. The motor consists of a rectangular stator (1.5 m long) with two air slots and three coils; two of them are fixed to the stator at the ends and one can freely move along the stator.
The fixed coils with currents I1 and I2 are the sources of two magnetic streams that have opposite senses from one to the other. A control current It in the mobile coil and magnetic field in the slots produce the driving force Fd. That force depends strongly and nonlinearly to the position x of the moved coil (Fig.1).
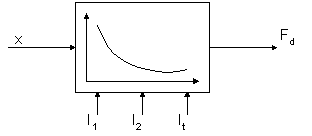
The goal of the authors was to construct a mathematical model of the linear motor to obtain the function of the driving force in relation to x and all the currents as parameters (Fig.1). The model is based on the assumption that electromagnetic system of the linear DC motor may be considered as a magnetic parameter distribution system.
To make the computed results come closer to reality,
it is proposed to apply the tuning model method off-line identification
(IOLMS) in the first step, and to construct the fuzzy logic model
of the driving force function.. Such approach allows adjustment
of the magnetic circuit parameters to minimize the difference
between the driving force function obtained from the model and
the measured one. It means that the move distance x should
be divided into a few parts (even if only two) with overlapping
limits. There should be the same model in each part but. However,
different parameters ought to be used. The identification method
is very efficient and guarantees very small approximation error.
25. Jarosław Guziński, Gdańsk
University of Technology
FUZZY LOGIC CONTROLLER OF INDUCTION MOTOR LOAD ANGLE
In the paper a new control system of an induction motor using multiscalar variables is presented. A simply current controller with voltage prediction was used in this system. The actual value of output voltage is evaluated with no delay time. Set values of stator current and voltage are used in control system in purpose to calculate a load angle and a rotor flux.
A phase locked loop was used to control an angle
between flux vector and stator current vector. A PI controller
was replaced with fuzzy logic controller. Theoretical considerations
are presented in the paper. The properties of the control system
have been verified by digital simulations using program in C.
26. Marcin Jaworski, Technical
University of Radom
STARTING OF STEPPING MOTOR IN FUNCTION OF VARIABLE COMMUTATION ANGLE - SIMULATION
The mathematical model of hybrid stepping motor and outcomes of simulations have been presented in the paper. The purpose of investigations was exploration of the influence of switching angle on the torque and the starting time of motor. As it has been shown in this paper, the change of the switching angle influences on the maximal electromagnetic torque produced by motor.
The way of commutation suggested in this paper allows
to better control the operation of motor. Through the change of
the commutation conditions it is possible to influence on the
work of gearing device, therefore this system is more versatile.
27. Janusz Juraszek, Arkadiusz Trąbka (Technical
University Łódz, Branch of Bielsko-Biała), Jan Nowak (Automotive Research and Development Centre
"BOSMAL")
ANALYSIS OF THE TEMPERATURE DISTRIBUTION IN FACE SEAL BY FEM
In this paper is presented analysis of the temperature distribution in hydraulically balanced face seal by Finite Element Methods. There were used axis symmetrical elements type Plane 55 and Ansys System FE. Boundary conditions based on Fourier and Dirichlet's conditions.
The numerical results obtained a good accordance
with the experiment. The temperature distribution is indispensable
to analysis of displacement and stress in face seal.
28. Tomasz Kaczmarek,
Kielce University of Technology
PROPAGATION OF ULTRA-SHORT LIGHT PULSES
Propagation of chirped solutions is discussed. The
Nonlinear Schrödinger Equation for complex initial conditions
is solved numerically. Numerical calculations confirm expectations
on an influence of the chirp magnitude on the pulse shape.
29. Tadeusz Kaczorek,
Warsaw University of Technology
AN EXTENSION OF THE GERGORIN'S THEOREM FOR REGULAR PENCILS
The classical Gergorin's theorem is extended for
regular pencils. The extension is based on application of the
elementary row and column operations to polynomial matrix of the
regular pencil. The extended Gergorin's theorem is illustrated
by an example. The extended Gergorin's theorem can be applied
in analysis and synthesis of generalized continuous-time and discrete-time
linear systems.
30. Iwona Karcz-Dulęba,
Wrocław University of Technology
DYNAMICS OF LARGE POPULATIONS' EVOLUTION IN GLOBAL OPTIMIZATION
This paper deals with the phenotypic evolution of infinite populations evolving in one-dimensional space. Of interest is the process of adaptation that leads to the global adaptive optima. The case of a bimodal fitness function, composed of two Bell-shaped quality hills, with the initial population normally distributed around the local optimum, is investigated. It can be demonstrated theoretically that the initial normal distribution of traits will be replaced by a sum of two normal distributions in the next generations. In the following generations each normal component will be split in two, again and again.
The cumulative effect of this process is investigated
using appropriate simulations. Simulation experiments show that
the distribution of population shifts towards the global optimum
and stabilizes in its vicinity but it still remains skewed toward
the lower peak. This process has been investigated for various
parameters of evolution and fitness function. The best identification
of global optimum was obtained with small values of modification
variation.
31. Jacek Karczewski, Mariusz Pawlak,
Institute of Heat Engineering in Łódz
SIMULATION OF FUNCTIONING POWER UNIT WHICH WORK IN REGULATION IN POLISH NATIONAL ENERGY SYSTEM
Computer model of power unit and numerical examples
related to real turbo-set have been presented. This model serve
as a instrument for testing of turboset electro-hydraulic microprocessor
control system (MREH). The controller was developed by the Institute
of Heat Engineering in Łódz. The analysis of
the controller's structure and the considerations of its functions
and units used are presented. Cooperation MREH with automatic
frequency and power control system (ARCM) have been shown on diagrams.
32. Jerzy Klamka, Silesian
Technical University, Gliwice
CONTROLLABILITY OF DYNAMICAL SYSTEMS WITH DELAYS
In recent years controllability problems for linear
retarded dynamic systems have been considered in many publications.
However, most literature in this direction so far has been concerned
with unconstrained controllability problems. Only a few papers
deals with the so called constrained controllability problems
i.e., with the case when the controls are restricted to take their
values in a preasigned set. Moreover, it should be pointed out,
that up to now constrained controllability of linear distributed
parameter systems with delays has not been considered in the literature.
Therefore, in order to fill this gap the present paper studies
the constrained controllability problem for abstract retarded
dynamic systems. The main purpose of the paper is to study constrained
controllability problems for linear time-invariant distributed
parameter dynamically systems with constant so called lumped delays
in the state variables. Dynamic system is described by linear
partial differential equation of parabolic type with zero Dirichlet
type boundary conditions. More precisely, constrained relative
approximate controllability and constrained absolute approximate
controllability are considered. Using some general methods taken
from the functional analysis, and specially from the spectral
theory of linear unbounded operators, several conditions for these
types of constrained controllability are formulated and proved.
Finally, some remarks and comments on the relationships between
relative and absolute constrained controllability are presented.
33. Mariusz Krawczyk,
Institute of Aviation, Warsaw
PREDICTION OF THE DYNAMIC CHARACTERISTICS AND AIRCRAFT CONTROL IN PRESCRIBED TRAJECTORY FLIGHT
A unified and general approach to the modeling and simulation of aircraft prescribed trajectory flight is presented. The program of motion is composed of a specified trajectory in space (two constraints on aircraft position), a demand on fuselage attitude with respect to the trajectory, and, optionally, a specification on the flight velocity. For an aircraft controlled traditionally by control surface deflections and thrust changes, it is shown that the realization of trajectory constraints is tangent, yielding two additional constraints on fuselage attitude.
A method for solving the equations is proposed. The
solution induced variations of aircraft state variables and the
demanded control that ensures the realization of the assumed program
of motion. This gives a unique opportunity to study the simulated
control strategies and evaluate feasibility of the modeled aircraft
missions. Some results of numerical simulation are reported.
34. Krzysztof Kula, Gdynia
Maritime Academy
IDENTIFICATION OF SHIP ROLL BY MEANS OF NEURAL NETWORK
Estimation of nonlinear stochastic system is an important
issue in the area of nonlinear control, system identification
and adaptive control. Conventional fin stabilization systems for
ship roll damping apply linear PDD2 controllers. Adjustment
of the controller settings. to the conditions is able to improve
their efficiency. This paper presents the concept of ship identification
as the object subjected to rolling by means of neural networks.
Constant observation of target value is the base for the design
of neural controllers. The structure and parameters as the neural
observer has been presented in this work. Computer simulation
of ship rolling identification at calm water and irregular waves
has been provided.
35. Andrzej Łodziński,
Warsaw Agricultural University
THE SUPPORT SYSTEM FOR MULTIOBJECTIVE CONTROL OF A MULTISTAGE PROCESS
In the paper the support system for multiobjective problem of a multistage process is presented. Multistage processes are those which differ in mathematical description in various parts of their control horizon called stages. In each stage there are many performance indices. Based on these indices, there is created one performance index for a given stage, using a scalarizing function, the minima of which depend on an additional parameter - the aspiration level.
Next, for each stage a local optimization of the stage performance index is carried out. These local optimizations are subordinate to a global optimization, which consists in the coordination of individual stages. In this way a multiobjective solution is obtained.
The choice of multiobjective control is made by solving
a problem with a changing parameter - a aspiration level, which
defines the user's requirements, and in assessing of received
solutions.
36. Włodzimierz A. Lubnauer,
Łódz University of Technology
DYNAMICS OF A MODEL OF TURBO-MACHINE WITH ELASTIC BEARING
In the article a mechanical system with the construction
similar to that of the turbo-machine or centrifuge models been
analyzed. The equations of motion have been derived, the numerical
analytic methods of solution have been given as well as the experimental
verification of the results.
37. Adam Marlewski, Stanisław Rawicki,
Poznań University of Technology
COMPUTER-AIDED SOLUTION OF DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS DESCRIBING ELECTRIC-DRIVE SYSTEMS
The means of solution of ordinary linear differential equations with trigonometric coefficients describing transient states in electromechanical systems is presented. Within the framework of the matrix state-space method, the equivalent infinite systems of differential equations with constant coefficients are introduced.
In the paper, the exemplary application of the authors mathematical method concerns the chosen case of an electrical machine containing a substitution single-phase winding both in the stator and in the rotor. Among others, this winding configuration exists in the single-phase alternating-current generator and in the zero-sequence system of the three-phase slip-ring induction machine.
Calculation results are compared with solutions obtained
by the classical Runge-Kutta way. In practical calculations, cut
of the infinite system is necessary; convergence of solutions
was verified for a different number of equations of the substitution
approximate mathematical model.
38. Andrzej Marusak, Warsaw
University of Technology, ISEP
VERY EFFICIENT SIMULATION OF MECHANICAL SYSTEMS WITH COULOMB FRICTION
Computer simulation of mechanical systems with coulomb friction procures some difficulties. Some people model the coulomb friction phenomenon as discontinuous function and meet with many problems, such as: very large integration errors, very long execution time, and small accuracy of simulation.
The author presents continuous model of coulomb friction phenomenon (CMCF). This model guarantees: very small integration errors, very fast simulation, and adequate accuracy of simulation. The CMCF is effective in simulation of system, with one coulomb friction element as well as with two or more coulomb friction elements.
Both simulation methods of coulomb friction have
been compared, and some results of simulations are reported.
39. Andrzej Marusak, Piotr Marusak,
Warsaw University of Technology
COMPUTER ANALYZERS OF FEEDBACK SYSTEMS - DEFINITION AND APPLICATION EXAMPLE
Simulators of dynamic systems are used mainly to appoint responses of systems on given inputs. Simulators are used besides to visualize received responses and to calculate coefficients that characterize quality of received responses. It is used in optimization process of system that is guided with support of responses received from simulator.
The calculation of transients is the most time consuming in simulator activity point of view. This calculation consists of solving of systems of differential equations. In the case of nonlinear system simulator with strong nonlinearities and with many feedbacks, the time of calculations of one response could be considerable. Therefore, during simulator constructing, the attention was paid mainly to obtain the most exact results in the shortest amount of time. This time, in spite of efforts, was the main limiter of simulated system optimization process efficiency.
The progress in computer technology (considerable increasing of calculation speed) makes wider approach to digital simulator application problem possible.
The authors propose building of dynamic system analyzers instead of simulators. System analyzer is stood up by adding an additional block to simulator - the block of researched system analysis.
The analysis block should work background of calculation, because most of time is used by simulator working. This problem is very good solved by multitasking of contemporary operating systems.
Analysis block could be more or less extended. Its task is to perform analytical calculations of researched system. For example in regard to system with feedback, analysis block could calculate: stability margin in given point of parameter space and in neighborhood of this point, chosen frequency characteristics, chosen parameters of frequency characteristics, stability region and the like. Analysis block accelerates decision processes during dynamic systems projecting with utilization of digital simulation. It enlarges observation horizon and gives more data on researched system.
An example of one-loop control system with PID controller
is presented in the paper.
40. Piotr Marusak, Warsaw
University of Technology, IAiIS
SYSTEM SUPPORTED PROJECTING AND RESEARCHING CONTROL ALGORITHMS WITH PLC AND OBJECT SIMULATORS
The system presented enables the projection and research of control algorithms for different objects. It is assembled from two PC computers which are connected with analog interface. Every machine is dedicated to run one of two currently elaborated simulators: simulator of very nonlinear electromechanical object and simulator of a control device. It is possible to replace one of the computers with a real object or real control device (e.i. Programmable Logic Controller).
The paper proposes a multistage way of making experiments.
It describes initial research made on one computer, and then continued
on two machines connected through the medium of cards of analog
signal converters. It presents a collaboration of computer with
simulator of object and PLC.
41. Jerzy Maryniak (Institute
of Aviation, Warsaw & Warsaw University of Technology),
Jacek Goszczyński (Institute
of Aviation, Warsaw), Andrzej Radlicz
(Warsaw University of Technology),
Jarosław Pyrz (Institute of Aviation,
Warsaw)
THRUST VECTORING CONTROL - AIRCRAFT DYNAMIC ANALYSIS IN 3D FLIGHT
Mathematical aircraft six degrees of freedom's model with thrust vectoring was presented in this paper. There was tested influence angle thrust vectoring on: a) deflection of elevator to guarantee of flight level, b) loop maneuver execute for two case apply a thrust vectoring.
Calculation was made for I-22 "Iryda" aircraft
as a test object. This work was supported by Polish State Committee
of Scientific Research (grant no. 9T12C 018 13).
42. Leszek Morawski, Mirosław Tomera, Gdynia
Maritime Academy
FUZZY MODEL REFERENCE LEARNING AUTOPILOT
This paper is concerned with an investigation into
the use of Fuzzy Model Reference Learning Control (FMRLC) to tune
fuzzy autopilot designs. The autopilots being used to control
the yaw dynamics ship model. Results are presented to show the
viability of such an approach and that effective design solutions
can be produced.
43. Jan Mućko, Technical
and Agriculture University, Bydgoszcz
STEP-DOWN PWM CONVERTER, QUASI-RESONANT AT SWITCH ON
In this paper a principle of operation, waveform
of current and voltage, mathematical description and characteristic
properties of this converter is described. This circuit can work
with fixed frequency. Regulation of voltage is possible to obtain
by a change of duty cycle D=ton/T. In a dependence
from duty cycle and a load there are 3 operation areas: area with
soft switching, area with soft turn on or soft turn off, area
with hard switching. A result of this paper can be helpful by
design of such converter.
44. Krystyna Myrcha, Jerzy Wróbel,
Central Institute for Labour Protection, Warsaw
THE SAFETY PROBLEM IN COMPUTER AIDED DESIGN OF MACHINE ASSEMBLIES
Problems of the design for safety in the computer
aided design of machine assemblies are becoming more and more
important. In the paper the grain combine - harvester is considered
as machine where safety problems are very important. The general
idea of CAD system, with safety criteria for this type of machine
has been formulated. The proper logical structure for the data
base oriented into safety problems in design is a first step in
CAD system creation. In the paper safety criteria are formalised
in a hierarchical way. As example in European Standard EN 292-1,2
"Safety of machinery; basic concepts, general principles
for design", some general ideas for design for safety and
general safety criteria are formulated. On a lower level particular
standards or regulations are formulated for a certain type of
machines or particular assemblies. In the paper the computer data
base with safety requirements for this type of machinery has been
created. This requirement results from Polish, European and international
regulations, directives and standards. This data base is dedicated
for designers of grain combine - harvester. This user friendly
computer data base is the important factor in the process of computer
aided design. The special organization of dialogue between the
designer and data base is proposed. This data base is connected
with data bases traditionally applied in design process. Data
base is created in MS ACCESS in WINDOWS environment and can be
directly linked to drawing editor - system AutoCAD. In the paper
some design results are presented.
45. Mieczysław Nowak, Roman Barlik,
Warsaw University of Technology
SIMULATION INVESTIGATION OF AC DRIVE WITH INDUCTION MACHINE SUPPLIED BY DC CURRENT LINK PWM CONVERTER
The simulation program prepared with PSI/e package
which permits a very accurate digital modeling of a whole relatively
very complex drive system is presented in the paper. The model
takes into consideration not only a line and motor converter function
with detailed PWM control but also a very accurately reconstructed
discrete control system. The control of PWM rectifier has two
different modes. At a modulation factor above 0.2 the phase is
constant and equal 0 (rectifier ) or 180 deg (inverter). At lower
modulation factor the DC current is controlled with current AC
wave phase angle displacement. Differential equations in Cartesian
co-ordinates including motor and capacitors voltages, currents
and fluxes are solved together with and inverter describing functions.
Additionally, an estimator of motor flux and load angle as a discrete
function block has been built in for more exact modeling of discrete
control system. The presented plots obtained as a result of simulations
show a very good quality of the model permitting investigation
of not only the long time constant process ( i.e. speed step response
) but also a very short time event ( in switching period time
constant ). The model should be very useful for real system control
implementation.
46. Grzegorz Oleszek,
High Pedagogycal School, Cracow
MEASUREMENT OF DYNAMIC PLANTAR FOOT PRESSURE WITH FSR SENSORS
The system for measurement of plantar foot pressure
has been developed. The study presents the efficacy of using Force
Sensing Resistors in determination of pressure map during dynamic
pressure. The FSRs are thick-film polymeric pressure sensors with
strongly nonlinear characteristics. To evaluate the pressure map
the mathematical model of the sensor has been presented. The verification
of that model was performed with Matlab in conjunction with experimental
data. Sensor's nonlinearity and temperature drift has been corrected.
Experimental results was obtained with measure of simple pressure
model, according to human foot. In addition, the plantar pressure
gradient has been calculated. High pressure gradients are thought
to be precursors to customary indications of plantar pressure
reduction.
47. Janusz Pospolita,
Technical University of Opole
SIMULATION OF OPTICAL FIBER WITH RAMAN GAIN
The beam propagation method (BPM) can be applied to an effective analysis of propagation characteristics, in nonlinear guides. The BPM enables analysis of arbitrary optical pulses propagating in any light guides, lossless as well as lossy, including Raman gain. All conclusions already known from theory of optical solitons have been proved so the results of computations seem to be correct.
The BPM is based on assumption that a guide can be
treated as a series of the fine lenses. Between them a homogenous
medium is assumed. All lenses are separated from each other by
the constant distance and each one imposes the phase front on
the beam. We are demonstrated propagation of 500 Gb/s
solitons with Raman gain over 30 km without signal regeneration.
49. Stanisław Rawicki, Przemysław Kaczorek,
Adam Marlewski, Poznań Technical
University
CALCULATION OF TRANSIENT STATES OF THREE-PHASE INDUCTION MOTOR WITH DOUBLE-SIDED ASYMMETRY
Some damages of a three-phase induction motor cause
the double-sided asymmetry, both in the stator and rotor circuit.
The expert analysis of the stator-currents components can be the
refined method which can discover the failure in great probability
also for such cases when the external effects of the defect are
indistinct (particularly at the beginning of the damage development).
At the double-sided asymmetry, the mathematical model of a three-phase
induction motor consists of differential equations with trigonometric
coefficients. For dynamic transient states, transformation of
the natural system of an induction motor to the substitutional
Lyon's time symmetrical components makes possible minimization
of structure of the mathematical model. For investigation of the
transient state at assumption of the constant rotor speed, the
authors method is employed; the system of differential equations
with trigonometric coefficients is replaced by the equivalent
infinite system with constant coefficients. Examples of simulation
results are given.
50. Andrzej Rusek, Andrzej Roman, Marek Lis,
Technical University of Częstochowa
SIMULATION DYNAMICALS CONDITIONS IN ROLLER TABLE BY MOTOR OF ASYNCHRONOUS TYPE SSP WITH MOTOREDUCER
The paper deals with simulation of dynamic states of a roll in a roller table used for a conveying system with a roller table motor and motorreducer.
Measurements of the dynamic states were carried out
on a laboratory stand reconstructing the actual dimensions of
the roll. For comparison, the kinematics system of the roll drive
was described by equations and dynamic responses for start-up
and load torque charge were calculated. The results skewed that
measured and calculated dynamic characteristics were similar in
both cases.
51. Janusz Skierski, Andrzej Oziemski,
Technical Uniwersity of Łódz
COMPUTER ADDED MODELLING OF RELIABILITY OF LARGE POWER UNIT DEVICES
Results of reliability investigations for 360 MW
lignite power units, carried out since the beginning of their
operation in Bełchatów Power Plant. Probability distributions
of the occurrence of failure times a and operation
times d were identified for main generating
units values of main reliability parameters: expected operation
time, expected intensity of failures, mean time of shut-down and
the total time of the shut-downs, were determined by the way of
estimation of probability distributions parameters.
52. Marcin Skowronek,
Silesian University of Technology, Gliwice
PSMA_WIN - ANALOG COMPUTER SIMULATION PROGRAM
The PSMA_WIN program is an example of a simple block oriented tool for creating models of continuous dynamic systems and executing simulation. Model description bases on the operational scheme and the model description file that lists the connections of the operational blocks and includes the additional directives (determining the model parameters values and experiment parameters values) and experiments initializing directives. The results of the experiments are saved in the results files. The PSMA_WIN offers three interfaces: - the interface for drawing the operational scheme and for generating the model description file, - the interface for simulation, that allows setting the model parameters and initializing an individual experiments as well as a sequence of the experiments, - the interface for graphical presentation of the experiment results.
The paper presents the basic feathers of the program,
the model specification rules, the possibilities of the interactive
mode and some examples of applications.
53. Włodzimierz Solnik, Zbigniew Zajda,
Wrocław University of Technology
SIMULATION OF CONTROL OF OXYGEN SATURATION PROCESSES
Replacement of the real intelligence by an "artificial"
one can lead to some exasperating consequences, even in the domain
of automatic control. Using the water aeration process as an example,
we demonstrate that the object's model, identified by a so-called
self-tuning intelligent controller, might be far from being
adequate. The implemented algorithms of self-tuning use to "assume"
that objects are linear and stationary. To avoid poor control
it is better to check carefully whether this assumption is really
satisfied.
54. Piotr Tatjewski, Robert Puz, Marcin Sikora,
Warsaw University of Technology, IAiIS
REAL TIME SIMULATOR OF DYNAMICAL PROCESSES
The paper presents short description of a real time simulator of continuous dynamic processes developed within the Process Control Research Group of the Institute of Control and Computation Engineering, Warsaw University of Technology. The simulator has been designed under the real time operating system QNX. The reason being the desire to have full control of time dependencies, in particular a guarantee that a modeled process respond to control signals and change its outputs precisely in a chosen real time scale. The inputs and outputs of the simulator program can be connected by the user to interface cards with A/D and D/A converters and I/O binary signals. Therefore, the simulated process can be controlled in real time from industrial controllers or another computer with control package installed, like SCADA systems with soft control modules or Matlab/Simulink with real time interface. Certainly, the simulated process can be visualized and operated in real time by a SCADA system.
The simulator has been designed under Photon graphical
environment, as a windows based user friendly package. Configuration
of the structure of the simulated process is performed using a
graphical screen, the mouse and a set of graphical buttons, similarly
as it is in Simulink. The process is composed from standard blocks:
set of differential eqs., set of difference eqs., transfer functions,
delays, gains, nonlinear elements, etc., including "user
blocks" containing any functions written by the user in C/C++.
Certainly, the simulator is equipped with sources of various signals
together with visualization and archiving capabilities. The program
can be run on PC computers under QNX.
55. Maria Trzaska, Warsaw
University of Technology
MATHEMATICAL MODEL AND COMPUTER SIMULATIONS OF THE PROCESS OF COMPOSITE COATING Ni-P-Al2O3
The paper aim is focused on investigations of Ni-P-Al2O3
composite coatings deposited by the currentless method on the
steel St3. To appropriate control of the process evolution for
manufacturing suitable coatings and for getting desired final
effects a mathematical model has been established. In this model
such important factors as electrolyte concentrations, orders of
the chemical reactions, activation energies and the process temperature
have been involved. The established mathematical model was used
to perform a series of respective computer simulations of the
time evolution of the studied process for various conditions of
its realizations. Comparisons of the obtained numerical results
with experimental ones have attested the correctness of the established
model. The results of numerical computations and experimental
investigations of the manufacturing of the composite coatings
are presented in form of corresponding diagrams and are documented
by appropriate images obtained by the scanning and optical microscopy
techniques.
56. Zdziław Trzaska, Warsaw
University of Technology
DYNAMICAL PROPERTIES AND APPLICATIONS OF TOTALLY POSITIVE SYSTEMS
The paper is aimed on studies of characteristic properties
of particular class of dynamic systems called in the sequel as
totally positive systems. Fundamental descriptions of the totally
positive systems are established and their dynamic properties
are analyzed. Relations between self frequencies and autonomous
oscillations of totally positive systems are involved. Special
attention is devoted to oscillatory systems and their applications
in such present high techniques as robotics and series capacitance
compensated electric power systems. Suitable illustrative examples
are presented.
57. Mirosław Wciślik, Jarosław
Patrzałek, Artur Pierściński,
Kielce University of Technology
COMPUTER STATION FOR SIMULATION OF DYNAMICAL OBJECTS IN CONTROL SYSTEMS
The paper deals with computer station for simulation of dynamical objects in control systems. The station can be used for programming and testing control algorithms for PLC controllers.
The station built using IBM PC computer and universal input-output card of analog and digital signals. Inputs and outputs of the card are connected to PLC controller outputs and inputs respectively.
The computer program simulates the object action. It generates the output signals in response of control signals (outputs) of controller. Taking account possibility of using Advantech SCADA software the I/O addresses of card are similar to the ones of Advantech PCL-711 card.
An example of dynamic object simulation using the
computer station is also presented.
58. Marcin Wyciślik,
Silesian University of Technology, Gliwice
COMPARISON OF METHODS OF NONLINEAR TIME SERIES ONE-STEP PREDICTION
This paper presents polynomial-based and neural methods
of identification of nonlinear time series. Polynomial methods
are represented by Group Method of Data Handling (proposed by
Ivakhnenko). Neural methods are represented by multilayer perceptron
trained by Levenberg-Marquard algorithm. A combination of these
methods is proposed and discussed.
59. Mieczysław Zając,
Instytut Energetyki, Warsaw
PARALLEL SIMULATION OF THE PERMANENT-MAGNET SYNCHRONMOTOR DRIVE
Some problems of parallel simulation problems of complex electromechanical system are discussed. The formalization of the design procedure is presented and simple multiprocessor system structure for control applications is described.
Parallel programming involves the distribution of
the due work among a number of T800 transputers, connected so
to form a network of some shape and size. To spread the simulation
work four T800 transputer were used. The implementation of parallel
algorithms on transputer nets results in considerable reduction
of computation time.
60. Zbigniew Zarzycki, Krzysztof Tusiński,
Technical University of Szczecin
SIMULATION OF TRANSIENT FLOWS IN TURBULENT LIQUID LINES
The mathematical model of liquid transmission lines
in the form matrix transfer functions have been presented in this
paper. Presented models refer especially to unsteady turbulent
flow. The distributed-parameter models were approximated with
the finite order models, by expressing the hyperbolic functions
in the form of infinite products. The application of the above
approximation for simulation of transient pressure has been shown.
61. Maria Złocka,
Warsaw University of Technology
SIMULATION OF THE DISTURBANCES OF AN AIRCRAFT MOTION AT HIGH ANGELS OF ATTACK
Mathematical models of the aircraft motion at high
angles of attack are very complicated. They usually have a non-linear
character. Some phenomena during the motion like, for example,
instability are undesirable. Application of the stabilizing controllers
is necessary for such the cases. The linear models of the motion
are necessary for synthesis of these controllers, however. And
here are meet a difficulty - linearisation of the equations of
the aircraft motion is non-acceptable. The non-linear controllers
have to be used. The difficulty appears during designing of the
optimal control. The proper Lyapunov's function should be guessed.
The question may arise: what is the effectiveness of such the
control with respect to linear sub-optimal control or non-linear
non-optimal control obtained using non-linear inverse dynamics?
In the paper the answer for such the question is given via simulation
of the controlled aircraft motion at high angels of attack. The
wing-rock is studied as an example. For such the motion aerodynamic
forces non-linearly depend on the disturbances of the flight parameters.
The computations are executed for an aircraft of F-16 type.


Copyright by Piotr Marusak
Uwagi na temat tej strony proszę przesyłać pod adres: s141892@ia.pw.edu.pl